In the internet world, most of us have heard of the term “contention ratio”. What is it? Why is it killing our internet? We’ll read all those matters that brainstorms in our mind when read such technical jargon.
First, Understand the Contention Ratio!
In layman’s term, the contention ratio refers to how many users are sharing the overall bandwidth and data capacity on an internet service provider’s dedicated line. To make this even easier, it’s a count of how many households are using the same main broadband line as you.
Technically, these are the data channels which are dedicated to us using a multiplexer (sometimes contracted to muxing), it is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium and travels to the infrastructure ends (switches and network devices) of the ISP.
This contention ratio affects the cost and class of internet you are getting at your home or office.
More contention means affordable and useable internet which we use at our home and buildings, less contention will not be affordable at all but there will be assurance of the speed and uptime, mostly used on businesses.
Usually a high speed internet connection is shared in ratios like 1:1 for leased line and large businesses, 1:2 ~ 1:10 for small businesses and small-mid enterprises, and 1:10 ~ 1:50 for home users.
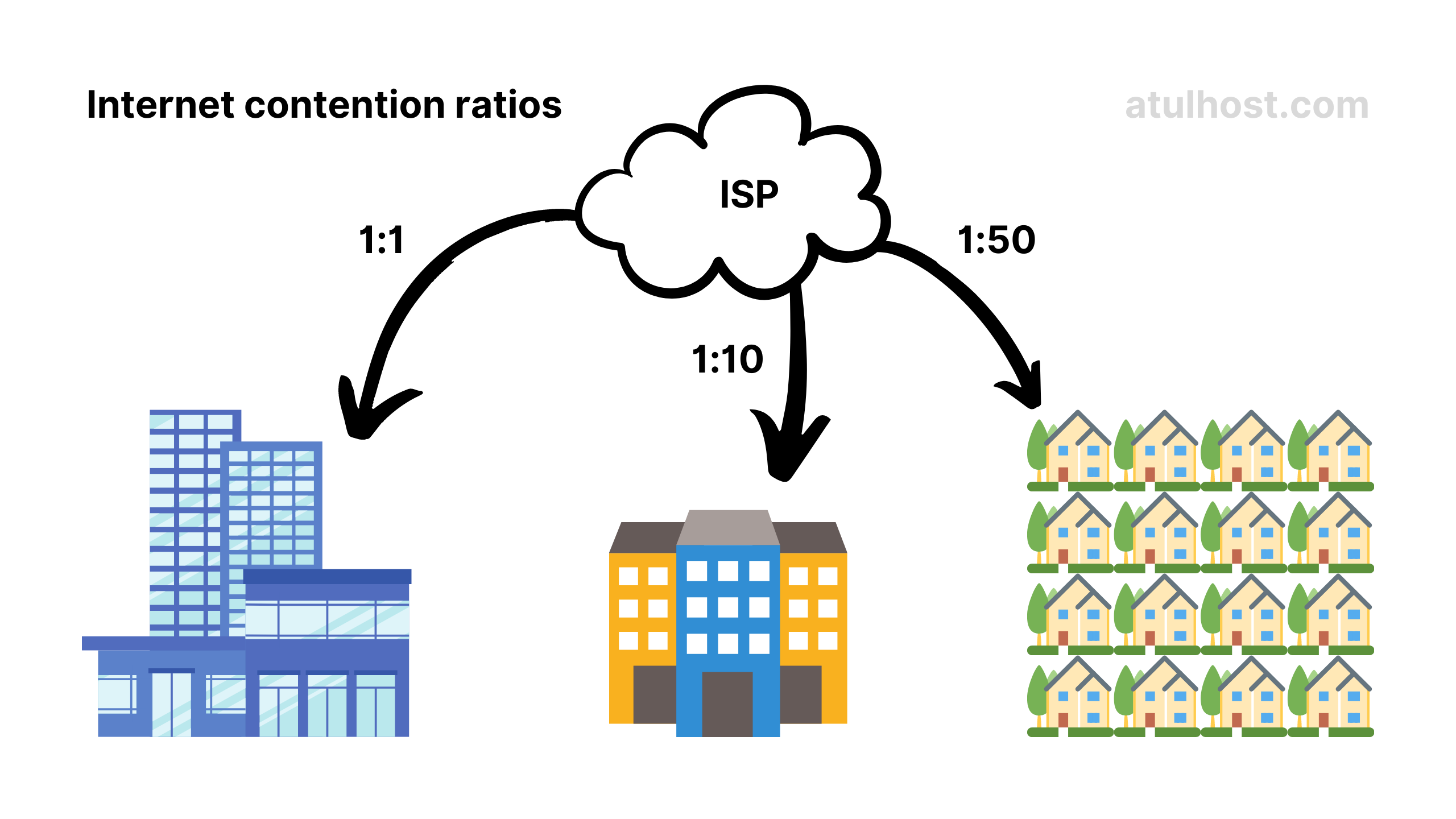
ISP can maintain any contention ratio, it is not fixed, but most of them share similarly.
Why Is It Killing Our Internet?
Contention ratio isn’t killing our internet but making things a way affordable to us. Except businesses, and corporates not everyone need superfast and 100% uptime guarantee, so ISP share this costly connection into multiple shared connections for home users, so common man don’t have to break his bank for simple internet access.
If you are getting your connectivity by fiber optics then there is no negative sign of contention ratio, but if you are getting your internet via other sources like copper, satellite, or wireless then there will be some performance downsides as other mediums aren’t capable of handling as many as data channels like fiber optics.
This is all, if you have any question or query in your mind let us know in the comments.
Leave a Reply