Although, batteries connected in Series versus Parallel will offer roughly the same amount of runtime, unless the load is different. In the series connection voltage increases and ampere remains same and in the parallel connection ampere increases and voltage remains same.
Many of us take advantage of both to increase capacity and voltage for a large backup system.
It often noticed that series connections provide a higher voltage, which is said more efficient for home use, where you’ll save more in wiring costs. This simply means that batteries wired in series can last marginally longer than batteries wired in parallel.
But a parallel connected battery will offer you marginally more backup, as capacity doubles when you add the second battery. The only limitation is you cannot run high-end machines, as heating issues due to high current use will make it inefficient compared to batteries connected in series connection. But for smaller setups with small load it is best.
Let’s understand the case with an example:
Here we took 12 Volts 150 AH inverter batteries to test this down.
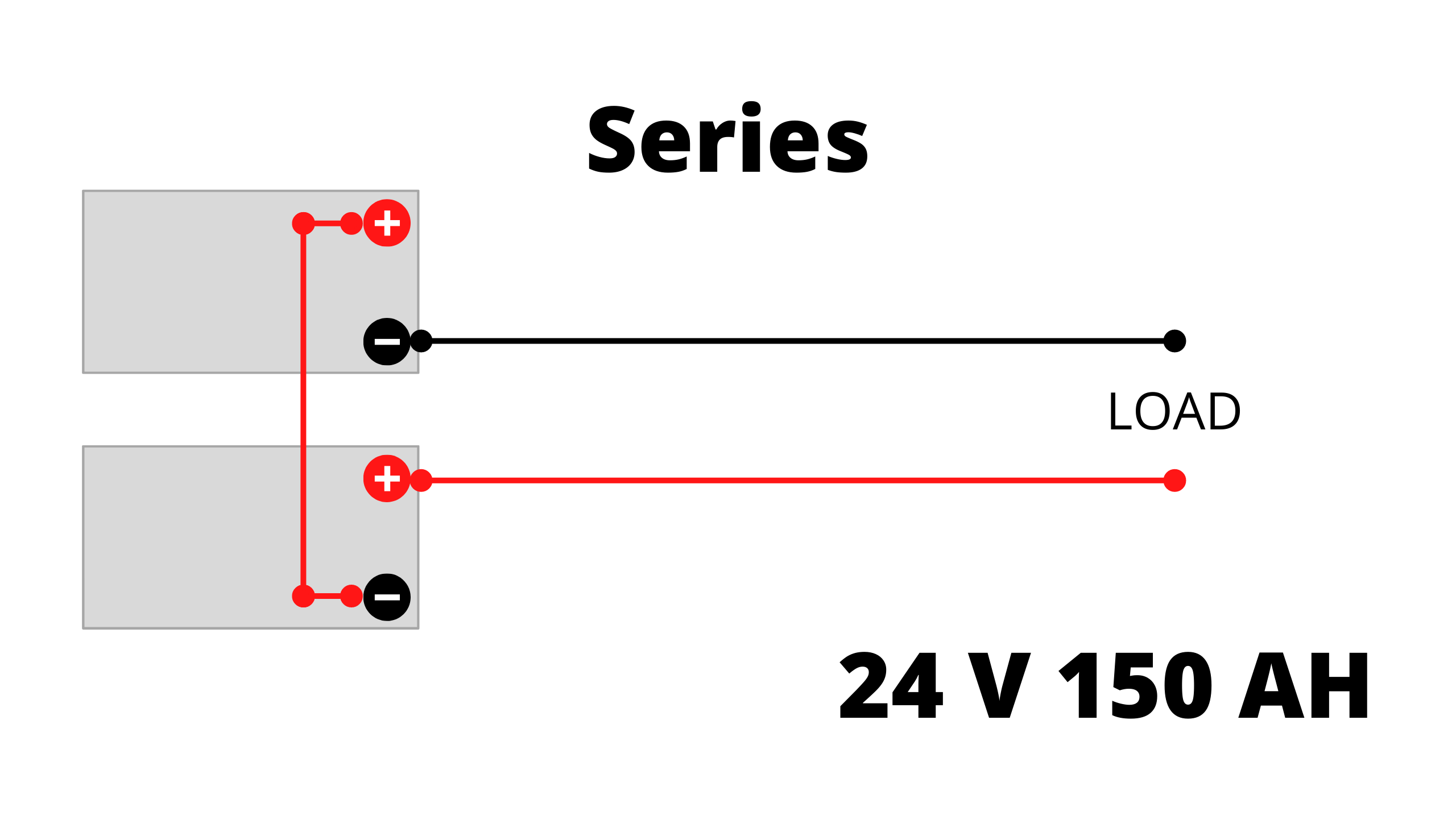
Series Connection:
In a series connection, you’ll get a total of 24 Volts and 150 Ah of capacity.
If you put a 360 watt load on it, the system will run for 10 hours.
Watt Hours = (12V×150AH)×2 Units = 1800×2 = 3600 Watt Hours.
Backup Time = 3600 Watt Hours/360 Watts = 10 Hours.- Series connected batteries do not overheat easily. It can be operated on normal wires.
- Series connection are easy to learn and to make, and higher voltage is good for all kind of setups and loads. But this will cost on batteries.
- It’s the single point of failure, if any battery stops working.
- Suitable for large setup with heavy load.
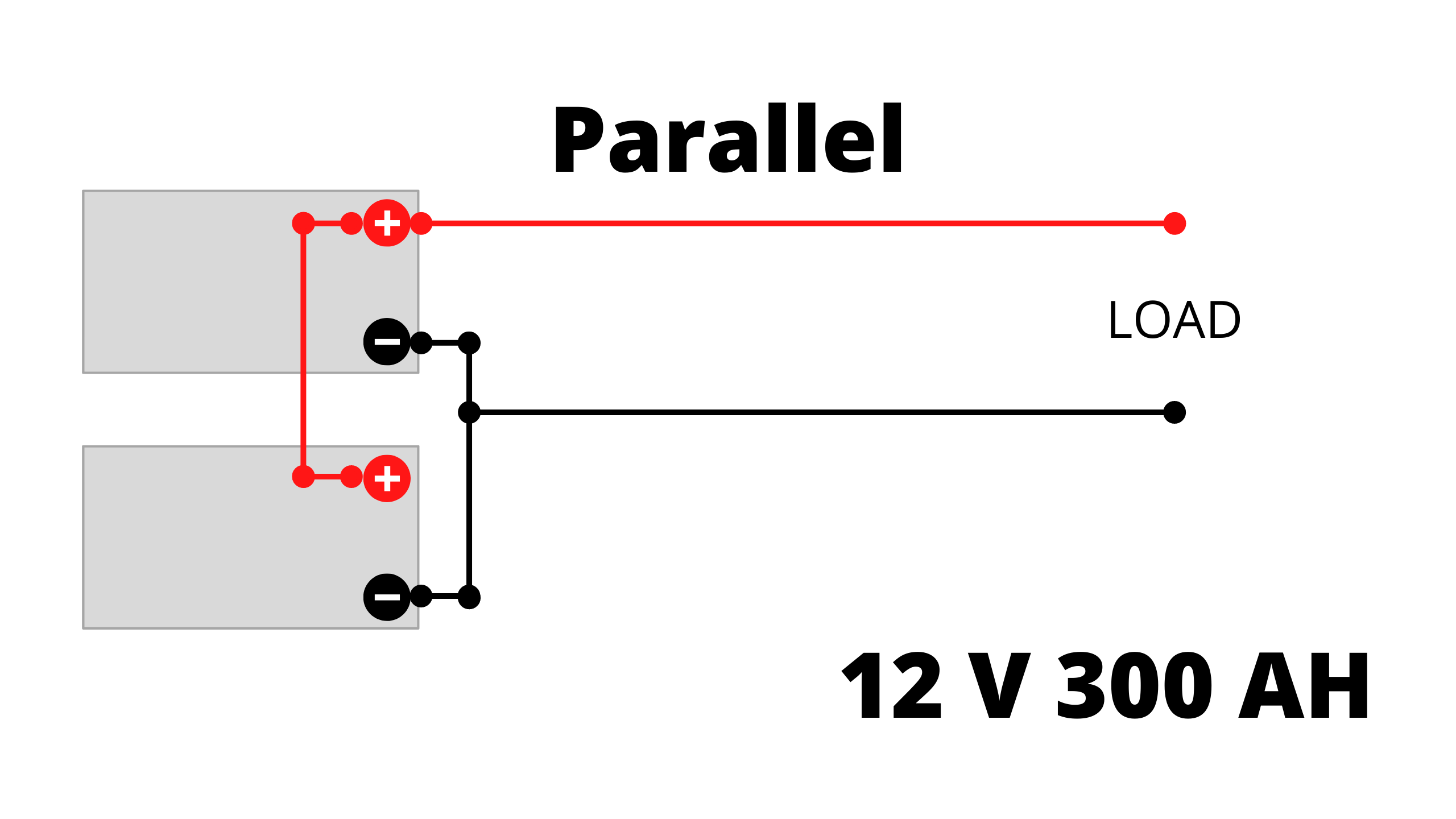
Parallel Connection:
In a Parallel connection, you’ll get a total of 12 Volts and 300 Ah of capacity.
If you put a 360 watt load on it, the system will run for 10 hours.
Watt Hours = (12V×150AH)+(12V×150AH) = 1800+1800 = 3600 Watt Hours.
Backup Time = 3600 Watt Hours/360 Watts = 10 Hours.- Series connected batteries do overheat easily, if you run more load on it. If the load is low and doesn’t need more watts, it is the best connection.
- Parallel connection is easy to learn and to make, but higher amps are dangerous to manage. Usually, we do not recommend joining batteries in parallel after a limit.
- If one battery stops working or gets faulty, simply remove it, it will work normally.
- Suitable for small setup with low load. Do not operate on high amps.
In conclusion, there is no such big difference unless you define a load that eliminates one system. Until there is any bottleneck or heating issues, you won’t notice any difference.
But for handling heavy loads, I’ll recommend series connection, which is safe.
Leave a Reply