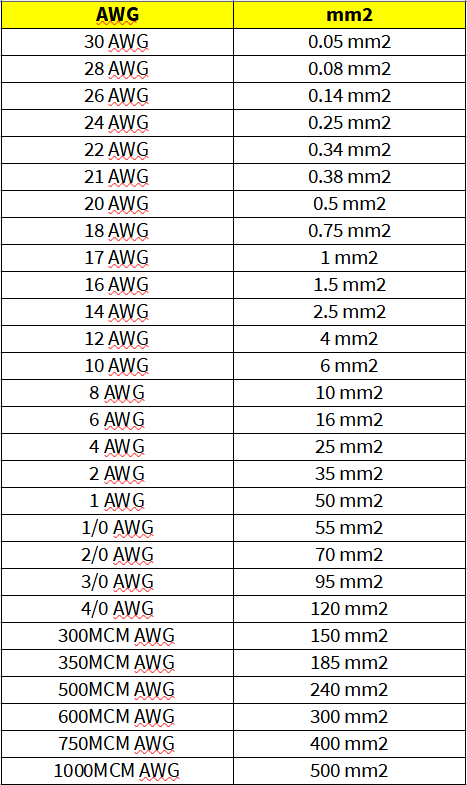
The electrical engineer makes a lot of calculations. Sometimes when an engineer visits a different country and his calculation may differ to a new country. Thus, here is a list of cross-reference AWG (American Wire Gauge) to mm2 (Square Millimeter).
Cross-reference AWG to MM2 chart.
| AWG | mm2 |
|---|---|
| 30 AWG | 0.05 mm2 |
| 28 AWG | 0.08 mm2 |
| 26 AWG | 0.14 mm2 |
| 24 AWG | 0.25 mm2 |
| 22 AWG | 0.34 mm2 |
| 21 AWG | 0.38 mm2 |
| 20 AWG | 0.5 mm2 |
| 18 AWG | 0.75 mm2 |
| 17 AWG | 1 mm2 |
| 16 AWG | 1.5 mm2 |
| 14 AWG | 2.5 mm2 |
| 12 AWG | 4 mm2 |
| 10 AWG | 6 mm2 |
| 8 AWG | 10 mm2 |
| 6 AWG | 16 mm2 |
| 4 AWG | 25 mm2 |
| 2 AWG | 35 mm2 |
| 1 AWG | 50 mm2 |
| 1/0 AWG | 55 mm2 |
| 2/0 AWG | 70 mm2 |
| 3/0 AWG | 95 mm2 |
| 4/0 AWG | 120 mm2 |
| 300MCM AWG | 150 mm2 |
| 350MCM AWG | 185 mm2 |
| 500MCM AWG | 240 mm2 |
| 600MCM AWG | 300 mm2 |
| 750MCM AWG | 400 mm2 |
| 1000MCM AWG | 500 mm2 |
You can save below image for your reference.
Leave a Reply